1961
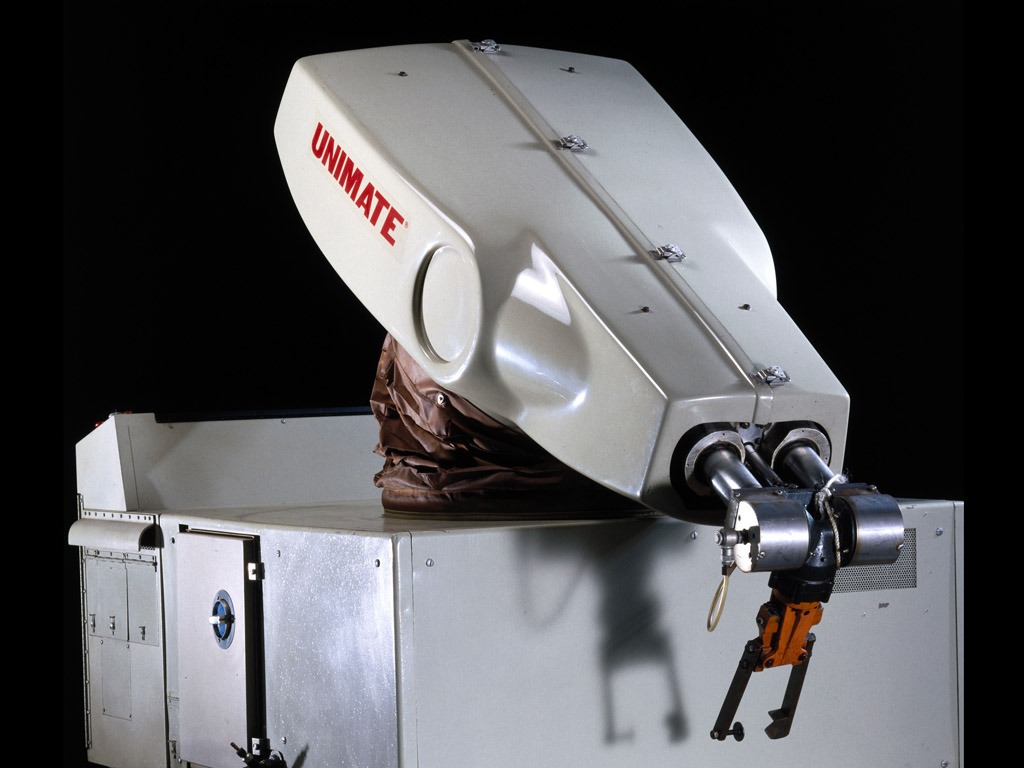

The first industrial robot, Unimate, starts working on an assembly line in a General Motors plant in New Jersey.
The history of Artificial Intelligence (AI) began in antiquity, with myths, stories and rumors of artificial beings endowed with intelligence or consciousness by master craftsmen. The seeds of modern AI were planted by classical philosophers who attempted to describe the process of human thinking as the mechanical manipulation of symbols. This work culminated in the invention of the programmable digital computer in the 1940s, a machine based on the abstract essence of mathematical reasoning. This device and the ideas behind it inspired a handful of scientists to begin seriously discussing the possibility of building an electronic brain.
Investment and interest in AI boomed in the first decades of the 21st century, when machine learning was successfully applied to many problems in academia and industry due to new methods, the application of powerful computer hardware, and the collection of immense data sets.
Ray Solomonoff was the inventor of algorithmic probability, his General Theory of Inductive Inference (also known as Universal Inductive Inference) and was a founder of algorithmic information theory. He was an originator of the branch of artificial intelligence based on machine learning, prediction and probability.

The first industrial robot, Unimate, starts working on an assembly line in a General Motors plant in New Jersey.
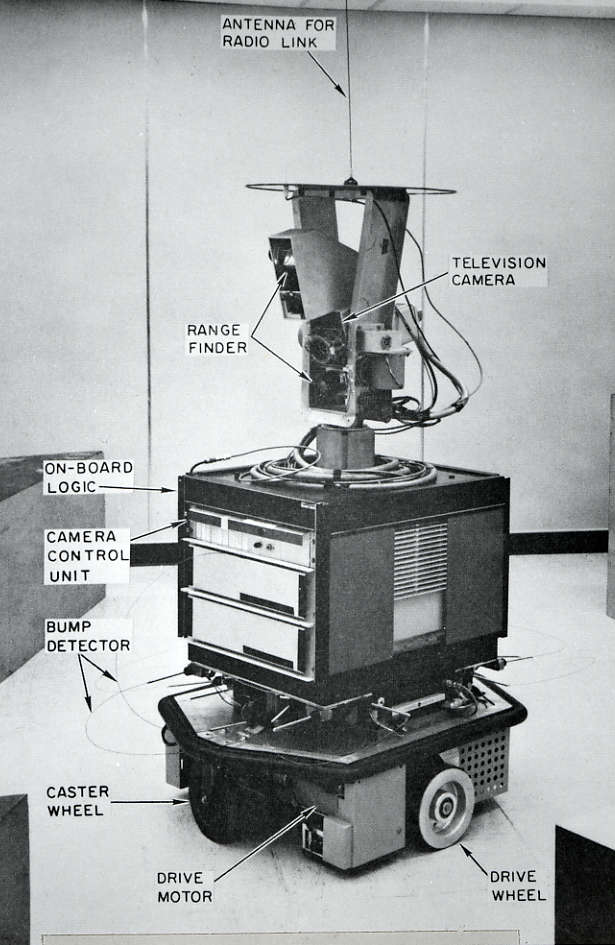
Shakey the robot is the first general-purpose mobile robot to be able to reason about its own actions. In a Life magazine 1970 article about this “first electronic person,” Marvin Minsky is quoted saying with “certitude”: “In from three to eight years we will have a machine with the general intelligence of an average human being.”

The film 2001: Space Odyssey is released, featuring Hal, a sentient computer.
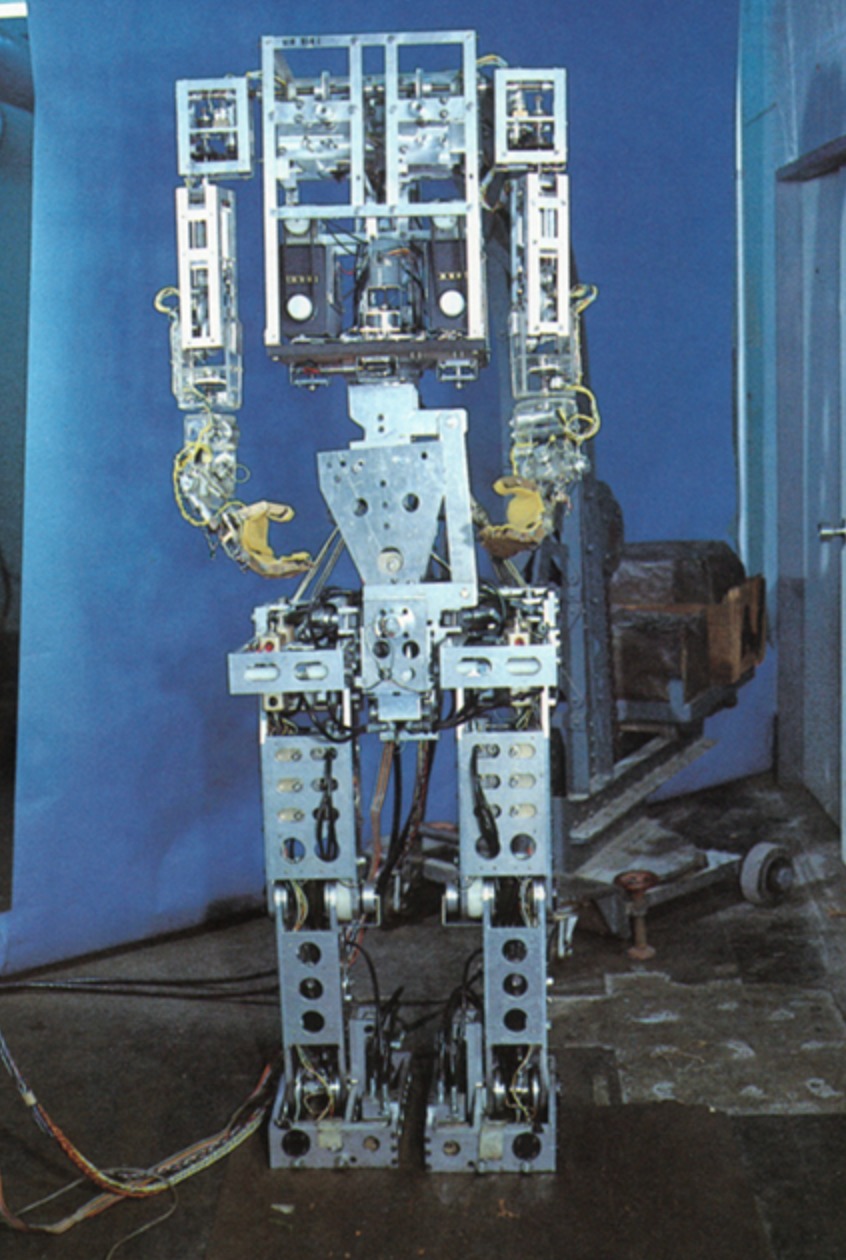
The first anthropomorphic robot, the WABOT-1, is built at Waseda University in Japan. It consisted of a limb-control system, a vision system and a conversation system.
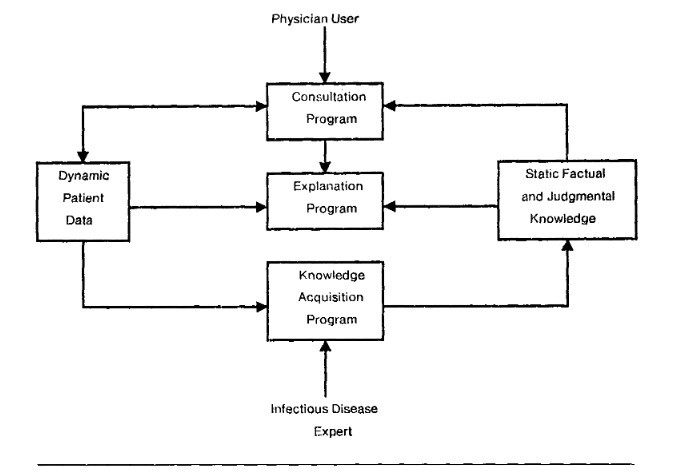
MYCIN, an early expert system for identifying bacteria causing severe infections and recommending antibiotics, is developed at Stanford University.

James Lighthill reports to the British Science Research Council on the state artificial intelligence research, concluding that "in no part of the field have discoveries made so far produced the major impact that was then promised," leading to drastically reduced government support for AI research.

Computer scientist Raj Reddy publishes “Speech Recognition by Machine: A Review” in the Proceedings of the IEEE, summarizing the early work on Natural Language Processing (NLP).
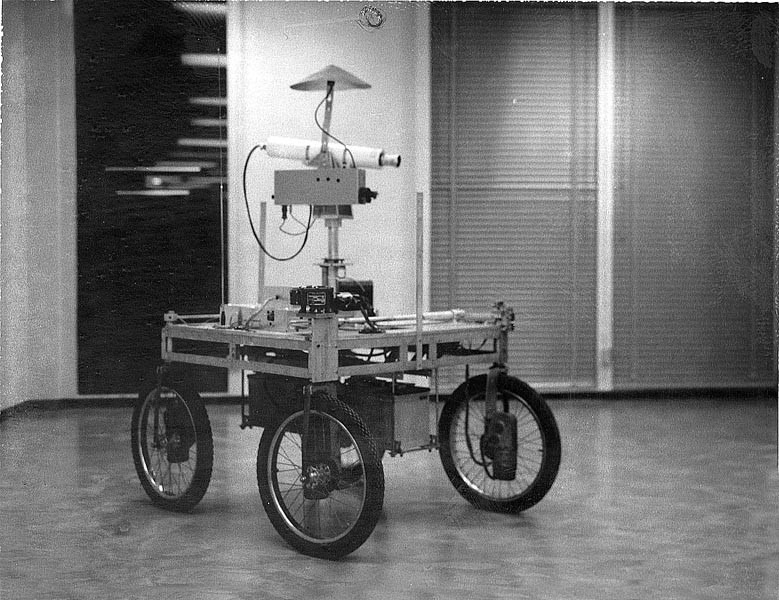
The Stanford Cart successfully crosses a chair-filled room without human intervention in about five hours, becoming one of the earliest examples of an autonomous vehicle.

Wabot-2 is built at Waseda University in Japan, a musician humanoid robot able to communicate with a person, read a musical score and play tunes of average difficulty on an electronic organ.

Electric Dreams is released, a film about a love triangle between a man, a woman and a personal computer.

First driverless car, a Mercedes-Benz van equipped with cameras and sensors, built at Bundeswehr University in Munich under the direction of Ernst Dickmanns, drives up to 55 mph on empty streets.
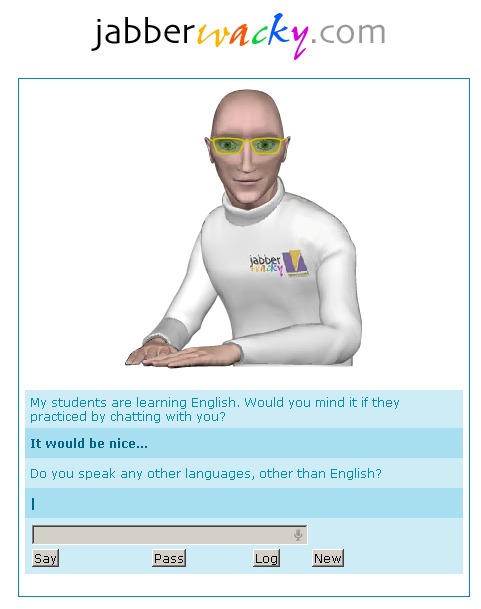
Rollo Carpenter develops the chat-bot Jabberwacky to "simulate natural human chat in an interesting, entertaining and humorous manner." It is an early attempt at creating artificial intelligence through human interaction.

Rodney Brooks publishes “Elephants Don’t Play Chess,” proposing a new approach to AI—building intelligent systems, specifically robots, from the ground up and on the basis of ongoing physical interaction with the environment: “The world is its own best model… The trick is to sense it appropriately and often enough.”

Richard Wallace develops the chatbot A.L.I.C.E (Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity), inspired by Joseph Weizenbaum's ELIZA program, but with the addition of natural language sample data collection on an unprecedented scale, enabled by the advent of the Web.
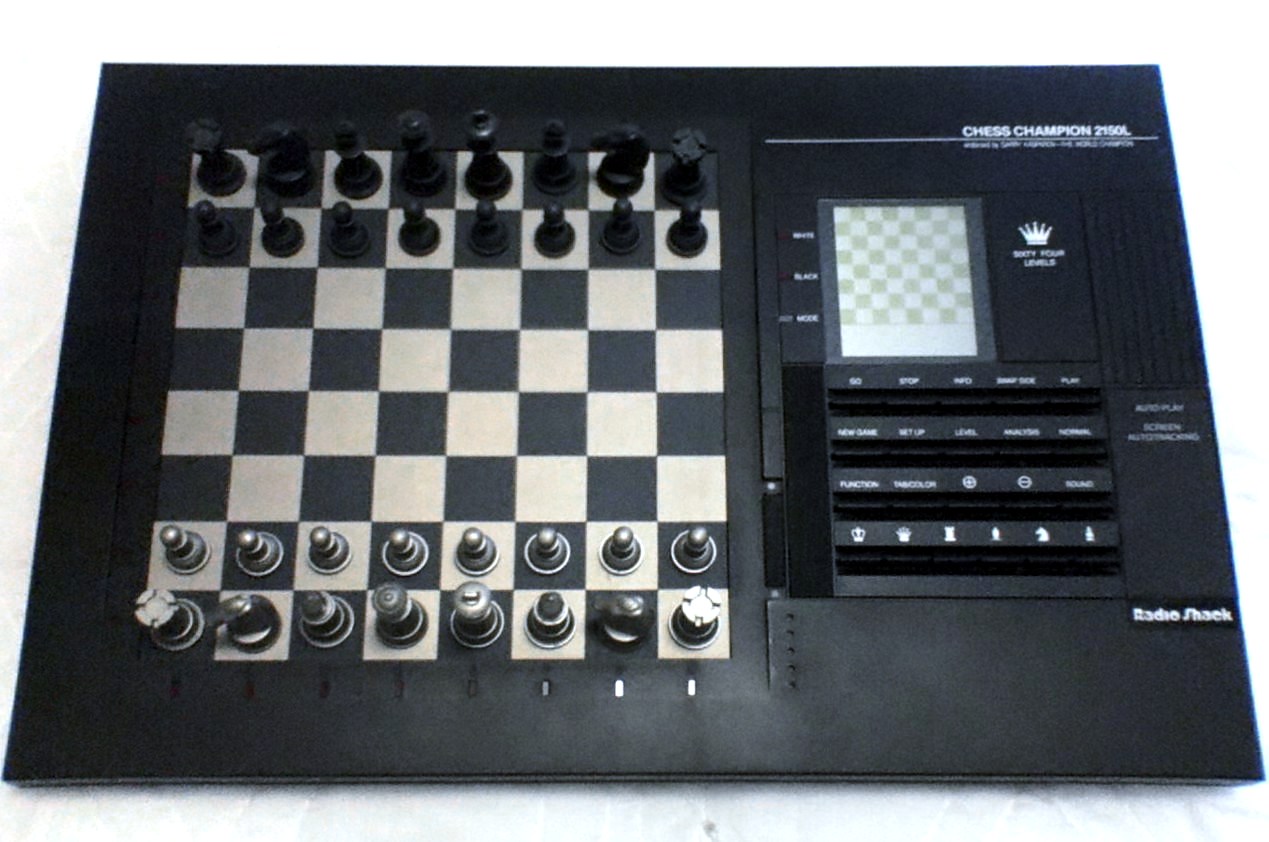

Deep Blue becomes the first computer chess-playing program to beat a reigning world chess champion.

Dave Hampton and Caleb Chung create Furby, the first domestic or pet robot.
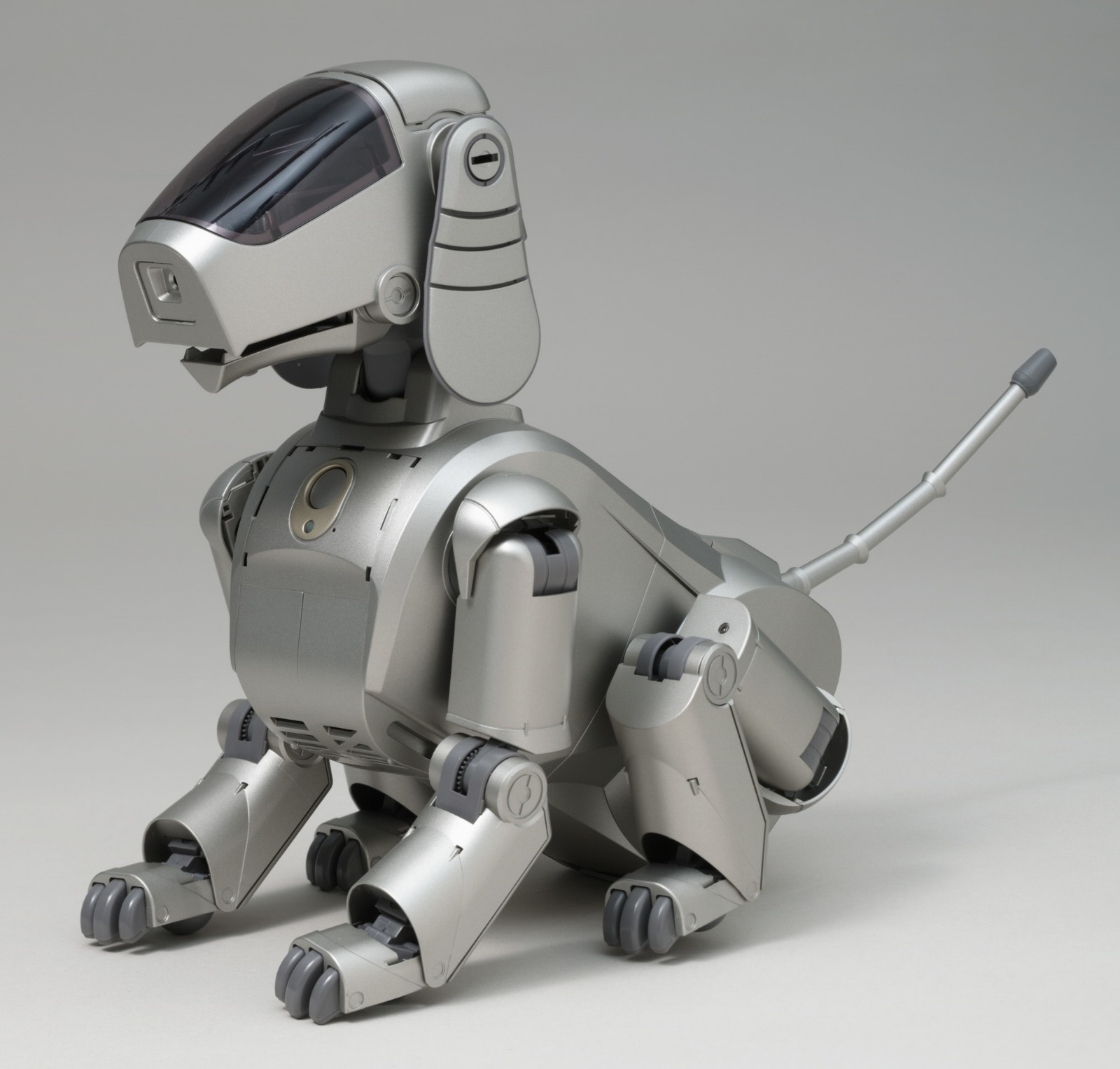

AIBO Sony launches first consumer robot pet dog AiBO (AI robot) with skills and personality that develop over time
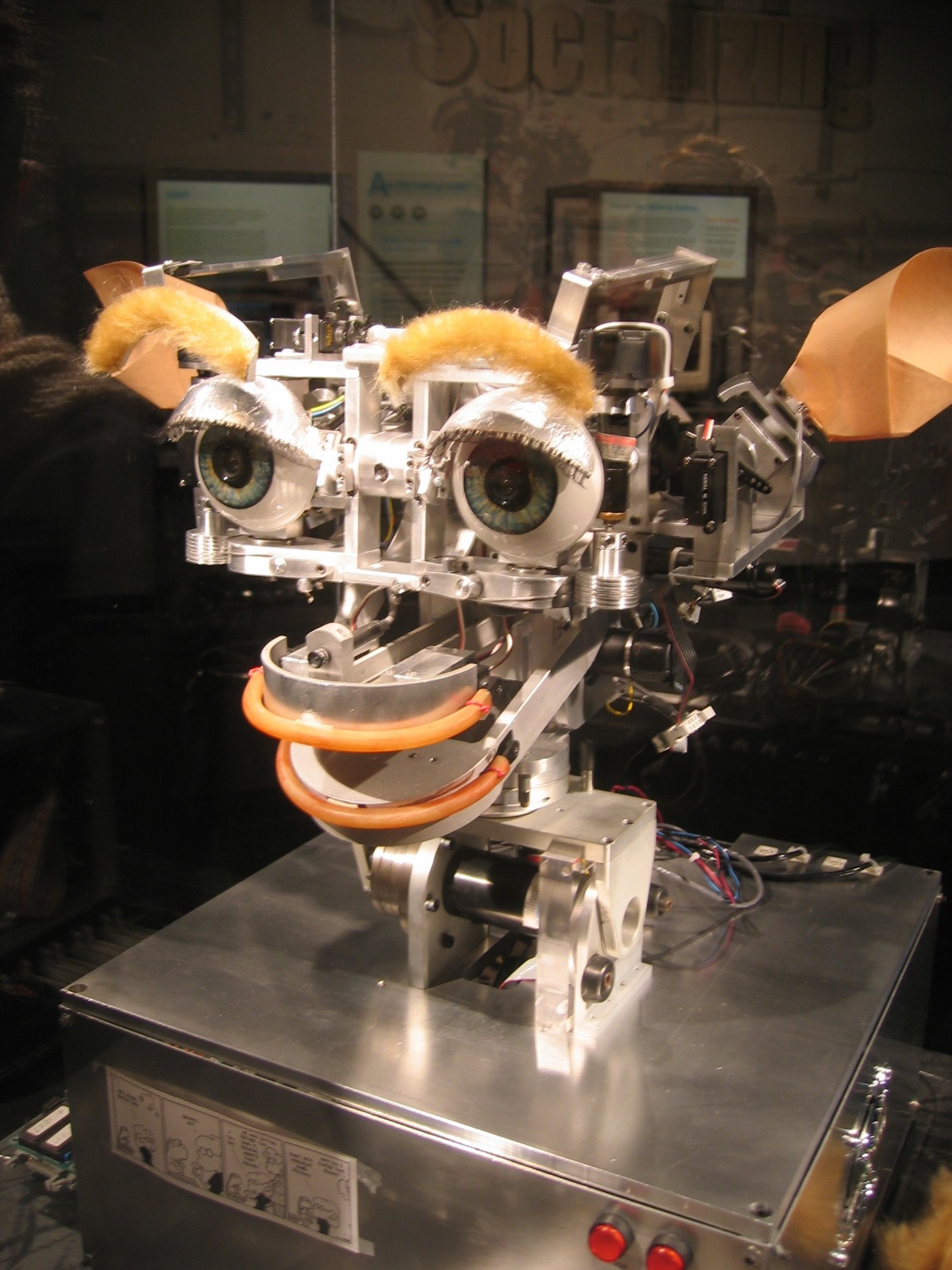
MIT’s Cynthia Breazeal develops Kismet, a robot that could recognize and simulate emotions.

A.I. Artificial Intelligence is released, a Steven Spielberg film about David, a childlike android uniquely programmed with the ability to love.
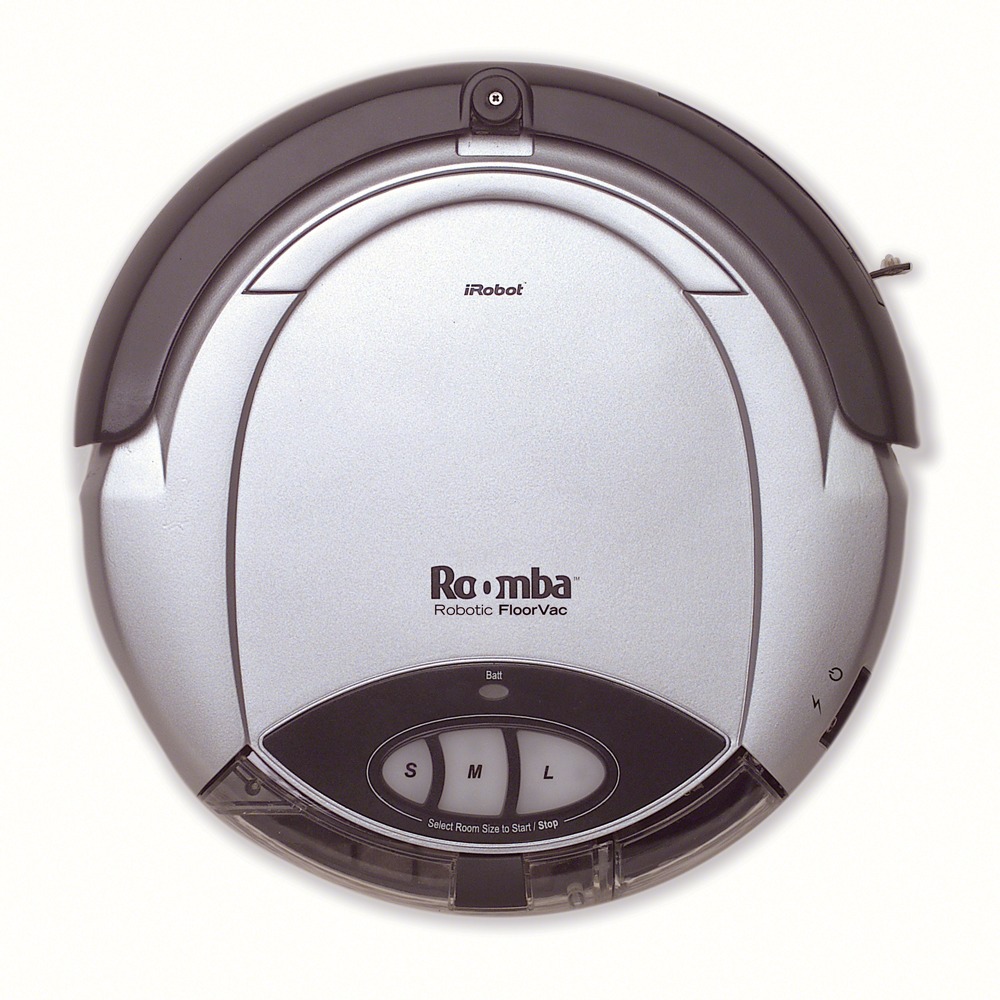

ROOMBA First mass produced autonomous robotic vacuum cleaner from iRobot learns to navigate and clean homes.
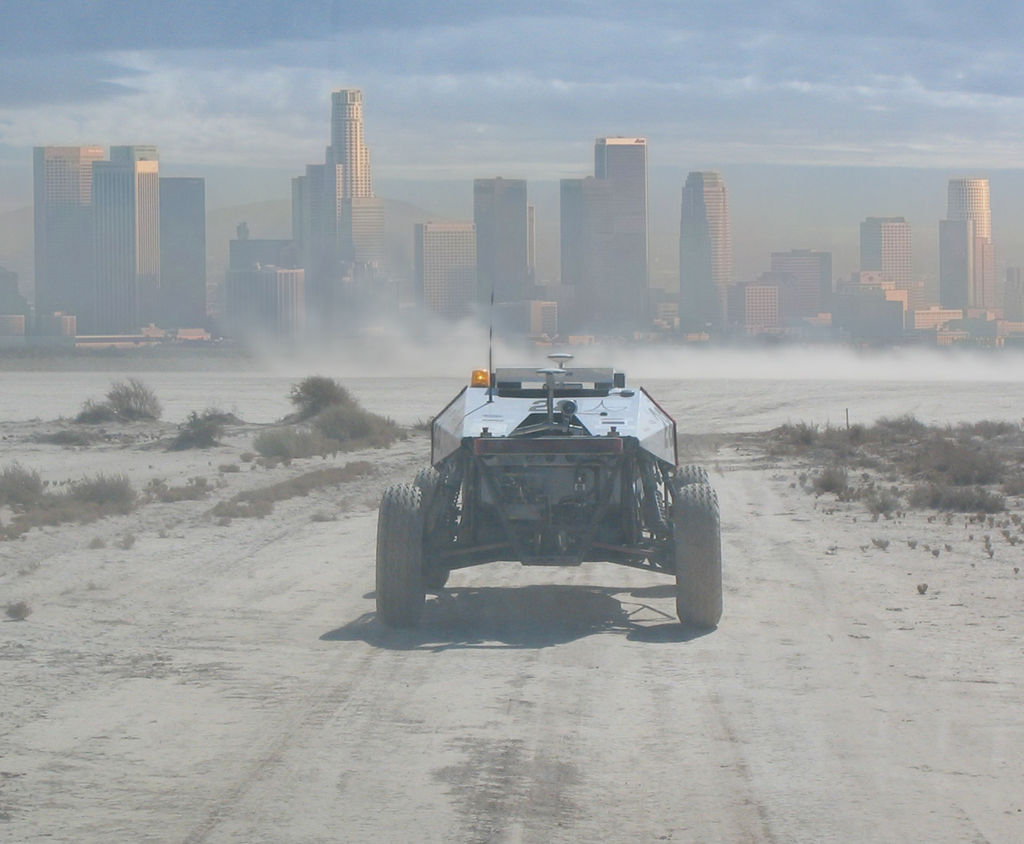

The first DARPA Grand Challenge, a prize competition for autonomous vehicles, is held in the Mojave Desert. None of the autonomous vehicles finished the 150-mile route.
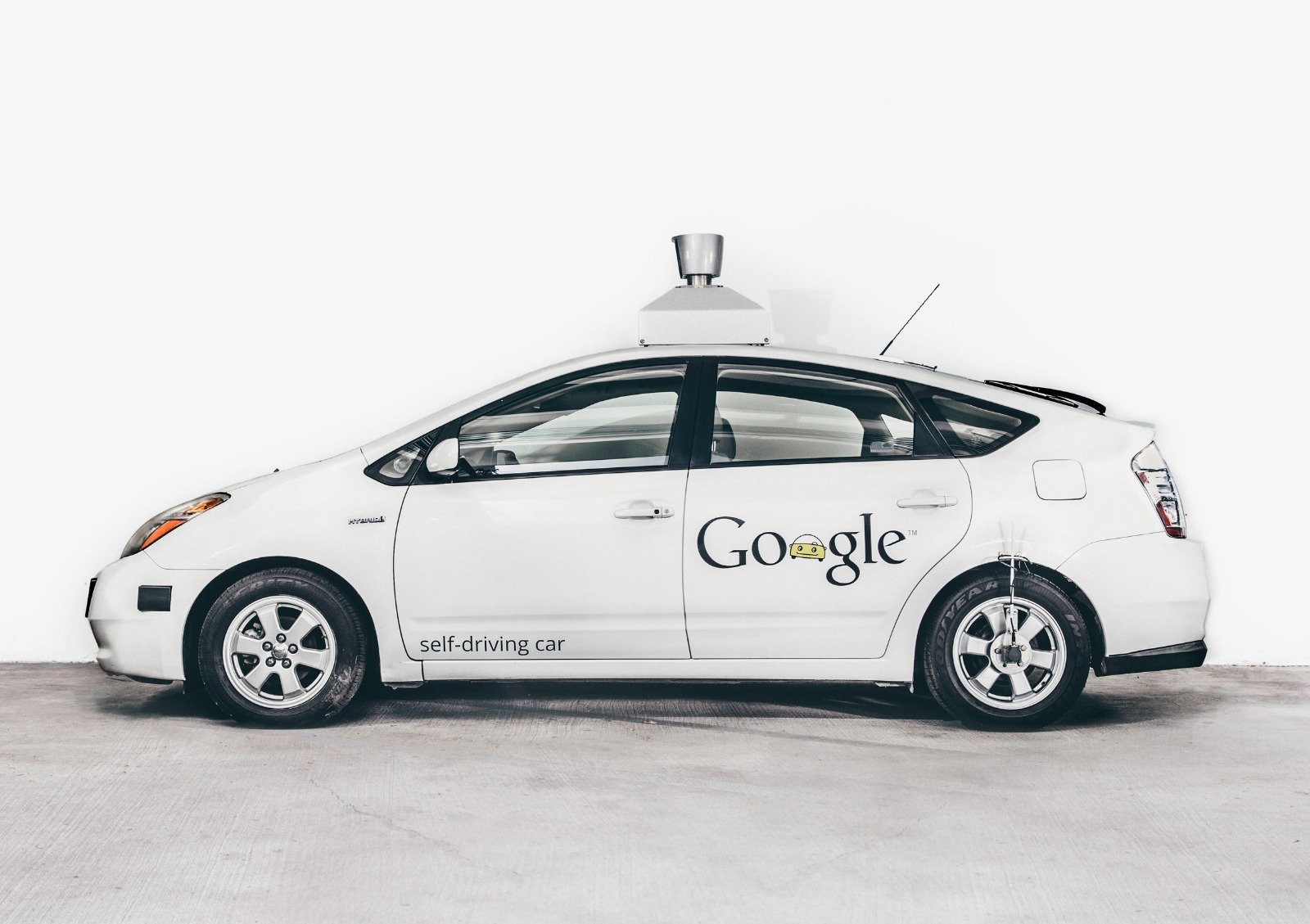

Google starts developing, in secret, a driverless car. In 2014, it became the first to pass, in Nevada, a U.S. state self-driving test.
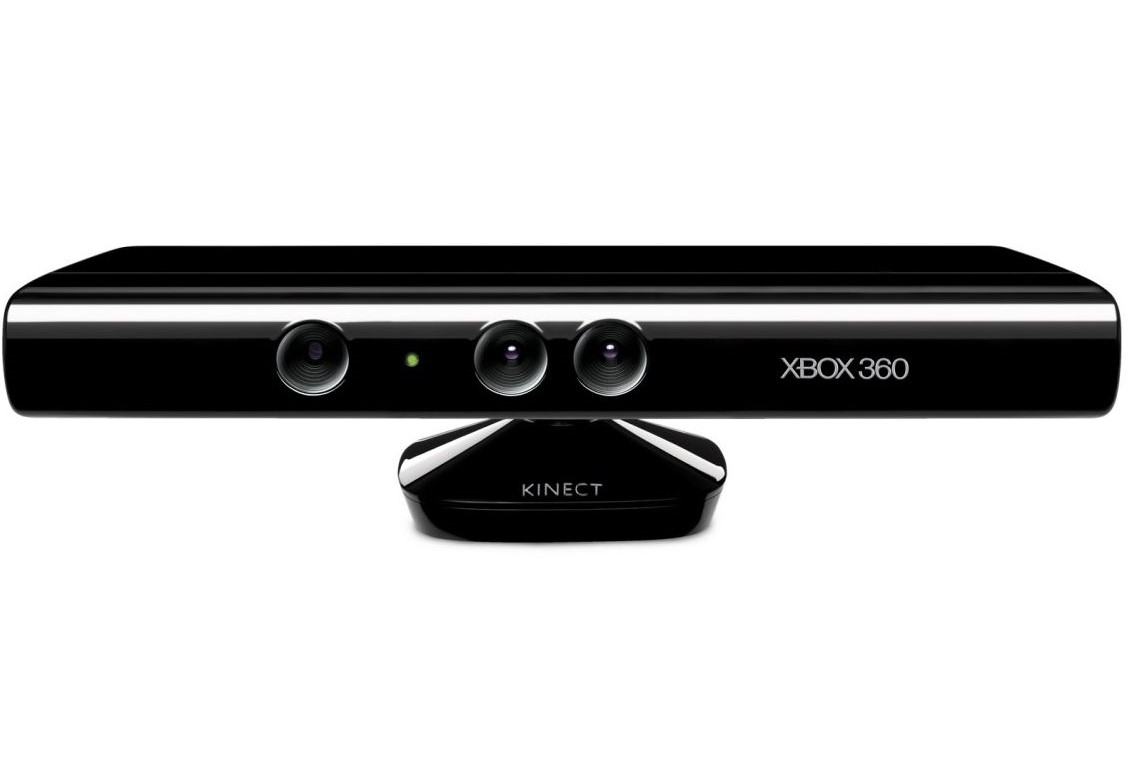

Microsoft launched Kinect for Xbox 360, the first gaming device to track human body movement, using just a 3D camera and infra-red detection, enabling users to play their Xbox 360 wirelessly. The award-winning machine learning for human motion capture technology for this device was developed by the Computer Vision group at Microsoft Research, Cambridge.

Apple announces voice activated Siri. A smartphone app that uses natural language to answer questions, make recommendations and perform actions.

Alexa is a voice associated with the Amazon Echo that will respond to questions and requests through artificial intelligence.
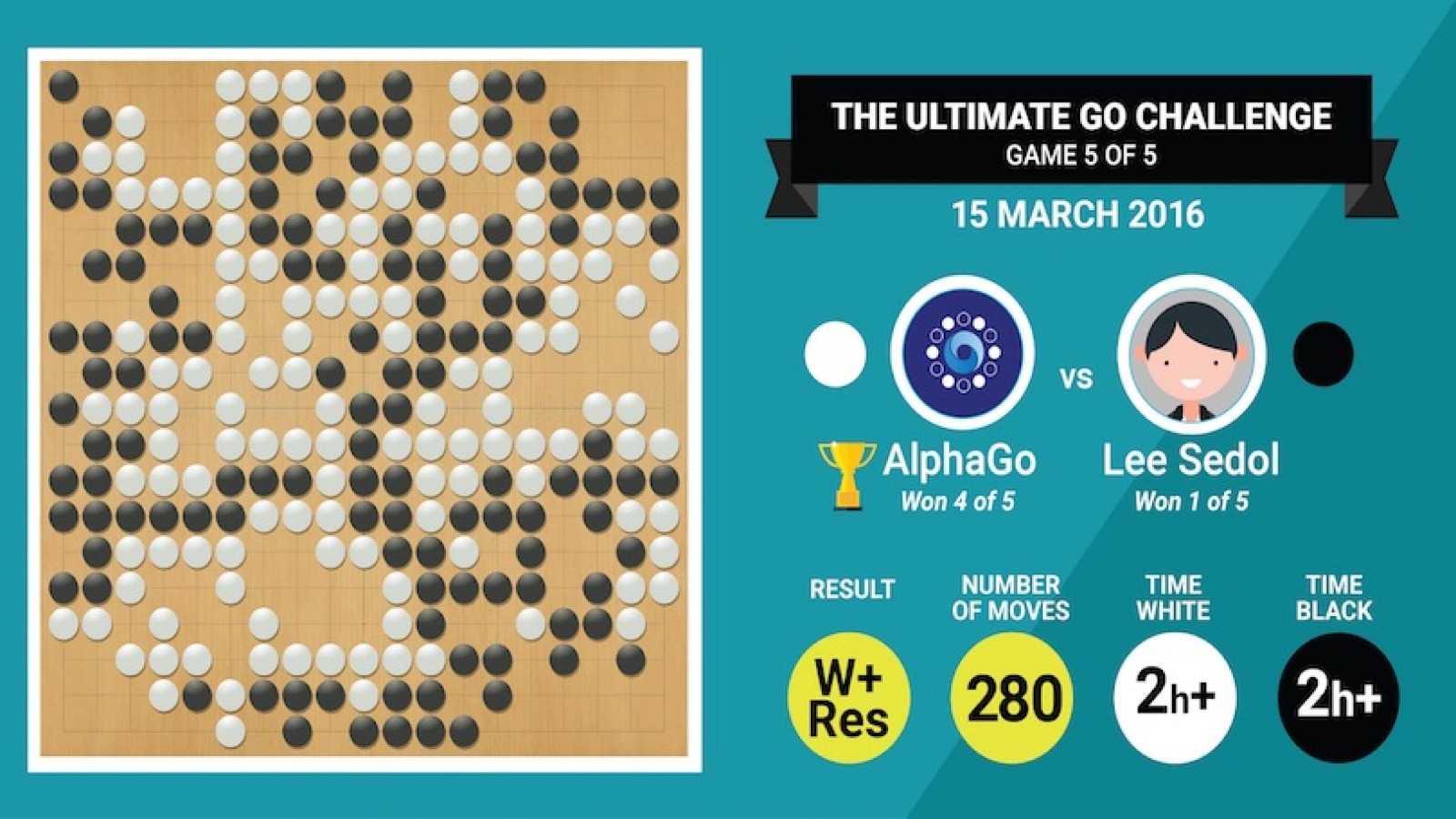
Google DeepMind's AlphaGo defeated Lee Sedol 4–1. Lee Sedol is a 9 dan professional Korean Go champion who won 27 major tournaments from 2002 to 2016. Before the match with AlphaGo, Lee Sedol was confident in predicting an easy 5–0 or 4–1 victory.
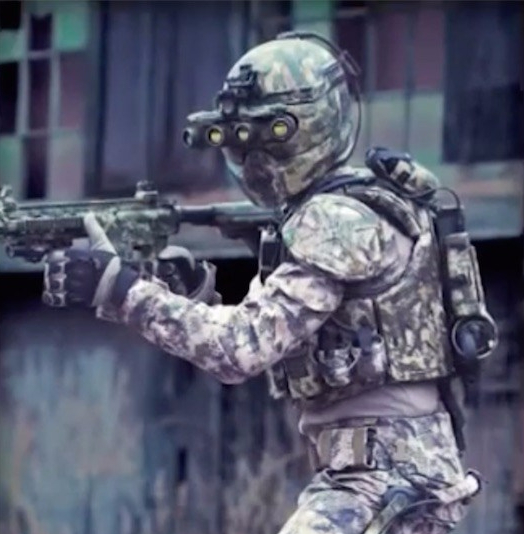

The United States Special Operations Command put forward the idea of the TALOS (Tactical Asault Light Operator Suit), a robotic exoskeleton to augment the soldier’s senses.
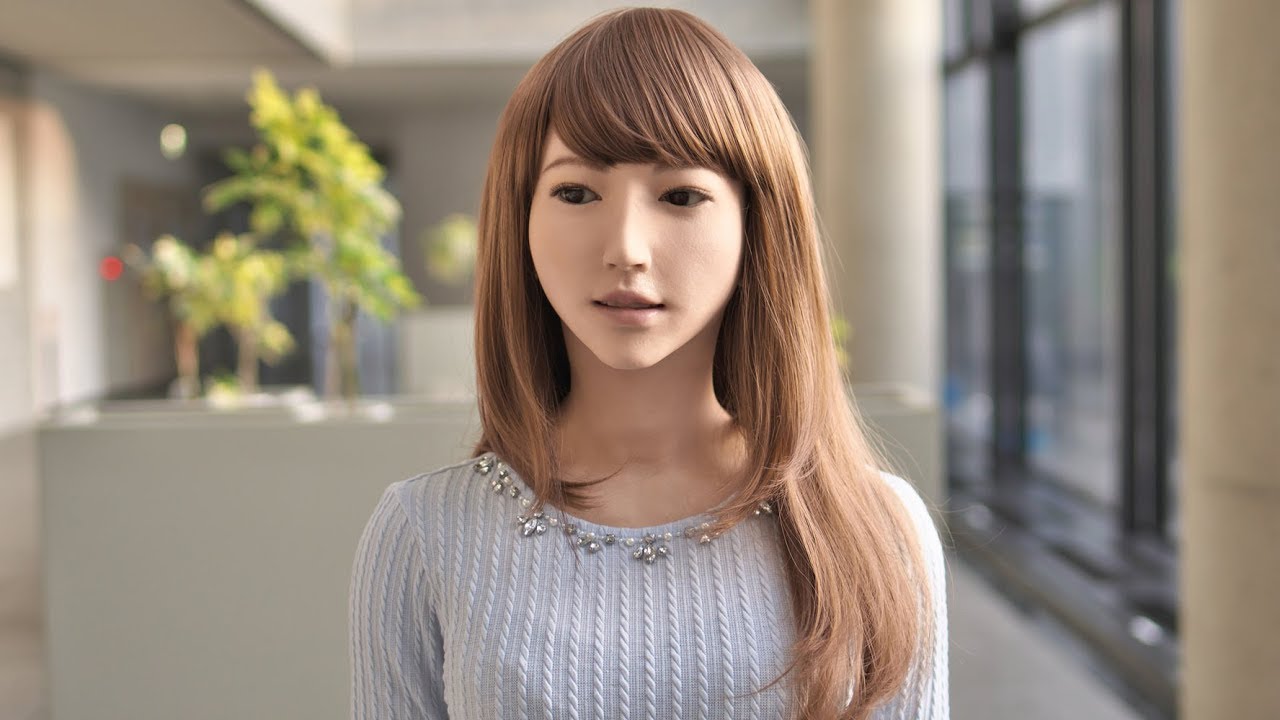

Erica, a Robot becomes a news anchor in Japan.